Resident Crews of the International Space Station (ISS)
![]()
ISS: Expedition 71 |
 |
 |
 |
crew poster |
![]()
Crew, launch- and landing data
| No. | Nation | Surname | Given names | Position | Spacecraft (launch) |
Launch date |
Launch time |
Spacecraft (landing) |
Landing date |
Landing time |
Mission duration |
Orbits |
| 1 | Kononenko | Oleg Dmitriyevich | ISS-CDR | Soyuz MS-24 | 15.09.2023 | 15:44:35.417 UTC | Soyuz MS-25 | 23.09.2024 | 11:59:03.8 UTC | 373d 20h 14m 28s | 5984 | |
| 2 | Chub | Nikolai Aleksandrovich | Flight Engineer-2 | Soyuz MS-24 | 15.09.2023 | 15:44:35.417 UTC | Soyuz MS-25 | 23.09.2024 | 11:59:03.8 UTC | 373d 20h 14m 28s | 5984 | |
| 3 | Dominick | Matthew Stuart | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-8 | 04.03.2024 | 03:53:38 UTC | SpaceX Crew-8 | 25.10.2024 | 07:29:02 UTC | 235d 03h 35m 24s | 3760 | |
| 4 | Barratt | Michael Reed | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-8 | 04.03.2024 | 03:53:38 UTC | SpaceX Crew-8 | 25.10.2024 | 07:29:02 UTC | 235d 03h 35m 24s | 3760 | |
| 5 | Epps | Jeanette Jo | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-8 | 04.03.2024 | 03:53:38 UTC | SpaceX Crew-8 | 25.10.2024 | 07:29:02 UTC | 235d 03h 35m 24s | 3760 | |
| 6 | Grebyonkin | Aleksandr Sergeyevich | Flight Engineer | SpaceX Crew-8 | 04.03.2024 | 03:53:38 UTC | SpaceX Crew-8 | 25.10.2024 | 07:29:02 UTC | 235d 03h 35m 24s | 3760 | |
| 7 | Dyson | Tracy Caldwell | Flight Engineer | Soyuz MS-25 | 23.03.2024 | 12:36:10.573 UTC | Soyuz MS-25 | 23.09.2024 | 11:59:03.8 UTC | 183d 23h 22m 53s | 2944 | |
| 8 | Wilmore | Barry Eugene "Butch" | Flight Engineer | CST-100 Boe-CFT | 05.06.2024 | 14:52:15.2 UTC | SpaceX Crew-9 | 18.03.2025 | 21:57:07.14 UTC | 286d 07h 04m 59s | 4576 | |
| 9 | Williams | Sunita Lyn "Suni" | Flight Engineer | CST-100 Boe-CFT | 05.06.2024 | 14:52:15.2 UTC | SpaceX Crew-9 | 18.03.2025 | 21:57:07.14 UTC | 286d 07h 04m 59s | 4576 | |
| 10 | Ovchinin | Aleksei Nikolaevich | Flight Engineer | Soyuz MS-26 | 11.09.2024 | 16:23:12.436 UTC | Soyuz MS-26 | 20.04.2025 | 01:20:33.5 UTC | 220d 08h 57m 21s | 3520 | |
| 11 | Vagner | Ivan Viktorovich | Flight Engineer | Soyuz MS-26 | 11.09.2024 | 16:23:12.436 UTC | Soyuz MS-26 | 20.04.2025 | 01:20:33.5 UTC | 220d 08h 57m 21s | 3520 | |
| 12 | Pettit | Donald Roy | Flight Engineer | Soyuz MS-26 | 11.09.2024 | 16:23:12.436 UTC | Soyuz MS-26 | 20.04.2025 | 01:20:33.5 UTC | 220d 08h 57m 21s | 3520 |
 |
Expedition Report
|
With the undocking of
Soyuz MS-24
on April 06, 2024 at 03:54:58
UTC the Expedition
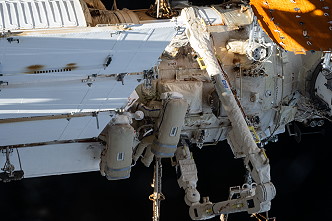
70 concluded the the new Expedition 71 began. On April 25, 2024 Oleg Kononenko and Nikolai Chub performed the first spacewalk in this expedition (4h 36m). Main tasks were to complete the deployment of one panel on a synthetic radar system on the Nauka module. The two cosmonauts also installed equipment and experiments on the Poisk module to analyze the level of corrosion on station surfaces and modules. A device for measuring engine exhaust emissions was realigned. Finally, the cosmonauts took swab samples from the outer hull of the Russian module. Following commands from ground controllers at SpaceX in Hawthorne, California, Dragon SpX-30 or CRS-30 undocked on April 28 2024 at 17:10 UTC from the forward port of the station's Harmony module and fired its thrusters to move a safe distance away from the station. After re-entering Earth's atmosphere, the spacecraft made a parachute-assisted splashdown off the coast of Florida at 04:38 UTC on April 30, 2024. In preparation for the arrival of NASA's Boeing Crew Flight Test, four crew members aboard the International Space Station relocated the SpaceX Crew Dragon spacecraft to a different docking port, on May 02, 2024, to make way for Boeing's Starliner spacecraft. Matthew Dominick, Michael Barratt, and Jeanette Epps, as well as Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Grebyonkin, undocked from the forward-facing port of the station's Harmony module at 12:57 UTC. The spacecraft then autonomously docked with the module's space-facing port at 13:46 UTC. The relocation, supported by flight controllers at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston and SpaceX in Hawthorne, California, freed up Harmony's forward-facing port for the docking of the Starliner spacecraft for its first flight with astronauts in May. Starliner will autonomously dock to the forward-facing port of the Harmony module, delivering Barry Wilmore and Sunita Williams to the space station. Progress MS-25 filled with 'junk' and used-up equipment undocked from the International Space Station on May 28, 2024 at 08:39:23 UTC. The unmanned transporter re-entered the atmosphere a few hours later and burned up over the South Pacific. Progress MS-27 launched on May 30, 2024 at 09:42:59.080 UTC from Baikonur. The unmanned spacecraft will deliver 2,504 kg of cargo into orbit, including 1,290 kg of apparatus and equipment for ISS systems, stowage for scientific experiments, clothing and food for the crew, 754 kg of fuel for refueling the station, 420 kg of drinking water, 40 kg of nitrogen to replenish the ISS atmosphere. Among the cargo is a hyperspectrometer for surveying the earth's surface in various spectral ranges (the Hurricane experiment). Also, on the Progress MS-27 are packages for the experiments "Biopolymer", "Interaction-2", "Virtual", "Correction", "Neuroimmunity" and "Pilot-T". After a two-day in-orbit journey to the station, the spacecraft automatically docked to the space-facing port of orbiting laboratory's Poisk module at 11:43 UTC on June 01, 2024. The spacecraft will remain docked at the station for almost six months before departing in late November 2024 for a re-entry into Earth's atmosphere to dispose of trash loaded by the crew. Launch of the ULA (United Launch Alliance) Atlas V rocket and Boeing Starliner spacecraft occurred at 14:52:15.2 UTC on June 05, 2024 from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The flight test carry Barry Wilmore and Sunita Williams to the space station for about a week to test the Starliner spacecraft and its subsystems before NASA certifies the transportation system for rotational missions to the orbiting laboratory for the agency's Commercial Crew Program. Starliner docked in a second attempt to the forward-facing port of the station's Harmony module at 17:34 UTC on June 06, 2024. U.S. spacewalk was cancelled on June 24, 2024 due to a water leak in the service and cooling umbilical unit (SCU) on Tracy Dyson's spacesuit. Tracy Dyson and Michael Barratt set their suits to battery power at 12:46 UTC and opened the hatch to the space station's Quest airlock before reporting the water issue. "Oh my goodness," said Tracy Dyson. "Water is flowing out of my SCU guys." "Yeah, there is a lot of particulates floating around here," added Michael Barratt. "There is water everywhere in here." "Tracy, if you can reconnect your SCU to the DCM [Display and Control Module], that is the best way to stop this," radioed capcom Stephen Bowen from Mission Control in Houston. Once Tracy Dyson reconnected her spacesuit cooling unit, the leak stopped but she had to deal with ice on her gloves and concerns about where other ice deposits had formed. Tracy Dyson closed the airlock hatch. Tracy Dyson and Michael Barratt worked with ground controllers to repressurize the crew lock section of the airlock before returning inside the station's equipment lock. This spacewalk had a duration of 31 minutes, officially ending 13:17 UTC. Tracy Dyson has now logged 23 hours and 20 minutes on four EVAs. Michael Barratt now has spent 5 hours and 37 minutes on three spacewalks. The plan was to recover a defective electronics box, prepare a spare elbow joint for the Canadarm2, and collect analytical samples from the Destiny and Quest modules. On July 12, 2024 at 11:01 UTC Cygnus NG-20 "S.S. Patricia "Patty" Hilliard Robertson" was unberthed from Unity nadir docking port released by the SSRMS. Flight controllers on the ground sent commands for the space station's Canadarm2 robotic arm to detach Cygnus from the Unity module's Earth-facing port, then maneuvered the spacecraft into position for its release. Michael Barratt monitored Cygnus' systems during its departure from the space station. Following unberthing, the Kentucky Re-entry Probe Experiment-2 (KREPE-2), stowed inside Cygnus, will take measurements to demonstrate a thermal protection system for the spacecraft and its contents during re-entry in Earth's atmosphere. On July 13, 2024 Cygnus NG-20 "S.S. Patricia "Patty" Hilliard Robertson" filled with trash packed by the station crew was deorbited and reentered the atmosphere. On August 04, 2024 at 15:02:53 UTC the unmanned freighter Cygnus NG-21 was launched on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. This spacecraft is named the "S.S. Francis R. "Dick" Scobee" after the late NASA astronaut. In addition to food, supplies, and equipment for the crew, Cygnus will deliver research, including supplies for a new STEMonstration and several test articles to observe water flow in microgravity. Other investigations aboard include vascularized liver tissue and a bioreactor to demonstrate the production of blood and immune stem cells. Researchers will learn more about biomanufacturing in microgravity to create higher quality treatments for people on Earth. NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative also is sending two CubeSats to deploy from the orbiting laboratory, CySat-1 from Iowa State University and DORA from Arizona State University, making up ELaNa 52 (Educational Launch of Nanosatellites). Cygnus arrived at the space station on August 06, 2024. Matthew Dominick captured Cygnus at 07:11 UTC using the station's robotic arm, and Jeanette Epps acted as backup. After capture, the spacecraft was installed on the Unity module's Earth-facing port. Progress MS-26 filled with 'junk' and used-up equipment undocked from the Zvezda service module of the International Space Station on August 13, 2024 at 01:50 UTC. The unmanned transporter re-entered the atmosphere a few hours later and burned up over the South Pacific. Progress MS-28 launched on August 15, 2024 at 03:20:18.472 UTC from the Baikonur cosmodrome. The unmanned spacecraft will deliver 2,621 kg of cargo: apparatus and equipment, stowage for experiments, fuel, nitrogen, clothes, water and food for the crew. Docking of Progress MS-28 with the Zvezda service module of the Russian segment of the International Space Station occurred on August 17, 2024 at 05:53:05 UTC. With undocking of unmanned CST-100 Boe-CFT Barry Wilmore and Williams Williams will continue their work formally as part of the Expedition 71/72 crew through February 2025. They will fly home aboard a Crew Dragon spacecraft with two other crew members assigned to the agency's SpaceX Crew-9 mission. Soyuz MS-26 docked to the International Space Station on September 11, 2024, at 19:32:08 UTC and delivered Aleksei Ovchinin, Ivan Vagner and Donald Pettit. Finally, the station command changed from Russian cosmonaut Oleg Kononenko to US astronaut Sunita Williams. With the undocking of Soyuz MS-25 on September 23, 2024 at 08:37:30 UTC the Expedition 71 concluded the the new Expedition 72 began. Soyuz MS-25 landed at 11:58 UTC with Commander Oleg Kononenko, Flight Engineers Nikolai Chub and Tracy Dyson. |
EVA data
| Name | Start | End | Duration | Mission | Airlock | Suit | |
| EVA | Kononenko, Oleg | 25.04.2024, 14:57 UTC | 25.04.2024, 19:33 UTC | 4h 36m | ISS-71 | ISS - Poisk | Orlan-MKS No. 5 |
| EVA | Chub, Nikolai | 25.04.2024, 14:57 UTC | 25.04.2024, 19:33 UTC | 4h 36m | ISS-71 | ISS - Poisk | Orlan-MKS No. 4 |
| EVA | Dyson, Tracy | 24.06.2024, 12:46 UTC | 24.06.2024, 13:17 UTC | 0h 31m | ISS-71 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3003 |
| EVA | Barratt, Michael | 24.06.2024, 12:46 UTC | 24.06.2024, 13:17 UTC | 0h 31m | ISS-71 | ISS - Quest | EMU No. 3013 |
Relocations of Manned Spacecrafts
| Spacecraft | from | Undocking | Time UTC | to | Redocking | Time UTC |
| SpaceX Crew-8 | ISS - Harmony PMA-2/IDA-F | 02.05.2024 | 12:57 | ISS - Harmony PMA-3/IDA-Z | 02.05.2024 | 13:46 |
Photos
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
onboard photos |
|
more EVA photos |
|
Earth observation photos |
|
| © |  |
Last update on January 07, 2026.  |
 |